In today’s digital world, cybersecurity for SMB (Small and Medium Businesses) is vital for small businesses to thrive, or at least survive. Cyber attacks continue to dominate the headlines, with a particular focus on well-known firms. However, research shows that small businesses with fewer than 100 employees are the target of 71% of cyber attacks. This demonstrates that small businesses are just as vulnerable as larger corporations.
Cybersecurity for SMB: Some Statistics
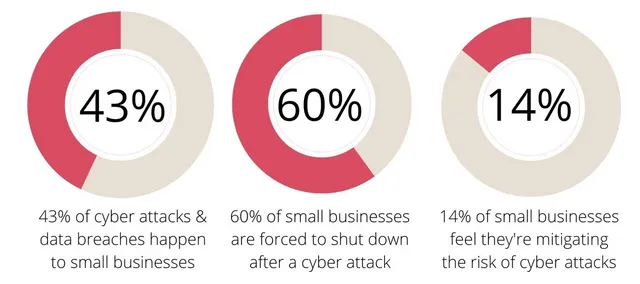
While we don’t aim to instill fear, it’s essential to recognize that small businesses face a higher likelihood of internal and external threats due to comparatively weaker network security than their larger counterparts. Cybersecurity firm Cobalt has compiled noteworthy statistics gleaned from reputable security surveys and studies, and we urge you to ponder them carefully:
- The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a staggering 600% surge in cybercrime.
- Small enterprises bear the brunt of 43% of all cyber attacks (Small Business Trends).
- The average cost of a cyber attack on a small business exceeds $25,000 (Readwrite).
- A mere 14% of small firms are adequately prepared to fend off cyber attacks (Embroker).
- Phishing/social engineering, compromised/stolen devices, and credential theft emerge as the most common types of assaults on small businesses (Forbes).
- In 2021, ransomware affected 37% of all businesses (Cloudwards).
- A new organization falls victim to ransomware every 14 seconds (Cloudwards).
- Phishing attacks contribute to a staggering 90% of all data breaches (Cisco).
- Social engineering is employed in 98% of attacks (Tribunal for hosting).
- Email is the source of 96% of all phishing attacks (Tessian).
- A striking 80% of small and midsize businesses do not employ data protection measures (Intel Security).
Even as a small business, it’s crucial to avoid the spotlight for the wrong reasons—particularly when it comes to the potential fallout from a devastating cyber attack.
Why is Cybersecurity Important for Small Businesses?
Theft of digital information has surpassed physical theft as the most frequently reported type of fraud, as highlighted by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). Despite operating on a smaller scale than larger corporations, small businesses should not dismiss the importance of cybersecurity as too advanced or unnecessary.
Contrary to assumptions, small businesses are not inherently immune to cyber threats. In fact, hackers often target them precisely because of the perceived lack of sophistication in their cybersecurity systems. Exploiting these vulnerabilities, cybercriminals gain easier access to computer systems, compromising valuable information and financial resources.
Beyond data theft, threat actors frequently employ ransomware attacks as a means of quick financial gain. These attacks involve holding a network hostage, restricting access to vital information until a ransom is paid.
Preserving brand reputation and avoiding ransom payments are paramount. The solution? Implement a comprehensive cybersecurity plan to shield your business from the ever-present risk of cyber attacks.
Why SMB are Easy Targets to Cyber Attacks
Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) often become prime targets for cyber attacks due to several factors. First, these businesses may operate with limited resources, leading to less sophisticated cybersecurity infrastructure. Hackers exploit this vulnerability, finding it easier to breach less fortified defenses. Additionally, SMBs may lack dedicated IT staff or cybersecurity expertise, making it challenging to stay abreast of evolving threats.
The perception that smaller businesses may not prioritize cybersecurity to the same extent as larger enterprises further attracts malicious actors. Furthermore, SMBs frequently collaborate with larger organizations as part of supply chains, offering cybercriminals a potential entry point to more extensive networks. The prevalence of valuable data, coupled with the misconception that smaller entities are less likely to invest in robust cybersecurity measures, makes SMBs enticing targets for cyber attacks.
In addition to limited resources and expertise, the interconnected nature of modern business ecosystems poses another challenge for SMBs. Small and medium-sized businesses often engage in collaborations, partnerships, or subcontracting with larger entities. While these relationships enhance business opportunities, they also introduce complexities in terms of cybersecurity. Cybercriminals recognize that breaching the security of an SMB can potentially provide a gateway to larger networks, amplifying the impact of their attacks. Moreover, the perception that SMBs may not prioritize cybersecurity awareness among their employees makes them susceptible to social engineering tactics.
Phishing attacks and other forms of manipulation exploit human vulnerabilities, capitalizing on the assumption that employees in smaller organizations may not be as well-trained to recognize and resist such threats. This combination of factors renders SMBs attractive targets for cyber attacks.
Cybersecurity for SBM: Why is it Vital?
Cybersecurity is crucial for small businesses for several compelling reasons:
- Protection of Sensitive Information: Small businesses often handle sensitive data, including customer information, financial records, and proprietary data. Cybersecurity safeguards this information from unauthorized access, protecting the business and its customers from data breaches.
- Financial Stability: Cyberattacks can result in significant financial losses. Small businesses may lack the resources to recover from the financial impact of a cyber incident, making preventive cybersecurity measures essential for maintaining financial stability.
- Reputation Management: A cybersecurity breach can tarnish the reputation of a small business. Customer trust is hard-earned and easily lost; a data breach or cyber incident can erode confidence, leading to a loss of customers and damaging the business’s long-term prospects.
- Legal Compliance: Many industries have regulations governing the protection of customer data. Non-compliance can result in legal consequences and fines. Small businesses need to implement cybersecurity measures to ensure compliance with relevant regulations and avoid legal issues.
- Operational Continuity: Cyberattacks, such as ransomware, can disrupt business operations. Implementing cybersecurity measures, including regular data backups and recovery plans, helps ensure operational continuity and minimizes downtime in the event of an attack.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Small businesses often have valuable intellectual property, such as trade secrets, patents, or unique business processes. Cybersecurity measures safeguard these assets from theft or compromise.
- Supply Chain Security: Small businesses are often part of larger supply chains. Cybersecurity is essential to protect the interconnected nature of business operations, ensuring that the security of one entity in the supply chain does not compromise others.
- Competitive Edge: Customers and partners increasingly prioritize cybersecurity when choosing whom to do business with. Small businesses with robust cybersecurity practices gain a competitive edge by demonstrating their commitment to protecting sensitive information.
- Employee Productivity: Cybersecurity measures, including training employees on best practices, contribute to a secure and efficient work environment. Employees can work with confidence, knowing that their actions align with cybersecurity protocols.
- Global Connectivity: In an era of global connectivity, small businesses are not immune to cyber threats originating from anywhere in the world. Cybersecurity measures help guard against international cybercriminals seeking to exploit vulnerabilities.
What Should SMB Top 3 Cybersecurity Priorities Be?
1. End-User Training
Prioritizing end-user training stands as the cornerstone of cybersecurity measures. The end user serves as the gateway to your network, and imparting basic cybersecurity knowledge is a cost-effective and time-efficient investment. Despite the advanced automation and cybersecurity software in place, employees remain one of the few elements beyond automated control. Their actions are inherently unpredictable, and regardless of the robustness of firewalls, it is the end user who can potentially circumvent these defenses.
Hence, it becomes paramount to ensure that employees comprehend what not to click on, exercise caution in downloading files, know the essentials of safeguarding company data, and adhere to sound password practices. This includes fundamental aspects such as avoiding the use of identical passwords across multiple applications or accounts.
Furthermore, instilling awareness about the importance of retaining data within the network and refraining from emailing personal information adds crucial layers to end-user training. Often taken for granted, these aspects are surprisingly misunderstood by many users. Even a modest amount of training can significantly enhance end-user understanding, reinforcing the overall cybersecurity posture.
2. Multifactor Authentication
Another crucial layer of defense is multifactor authentication (MFA), which plays a vital role in securing your network and safeguarding critical data, such as your email network and essential CRM infrastructure.
You’ve likely encountered MFA before, perhaps with your bank, where they send a pin number to your cell phone for verification when logging into your online account portal. Implementing a similar, yet simpler, MFA system for your CRM, email, remote network access, and other critical systems is essential. The goal is to ensure that your MFA is user-friendly, and a mobile app often proves to be the most effective solution.
In this setup, when a login attempt is made, the app prompts the user with a simple question: ‘Is this you?’ The user responds with a green checkmark for ‘yes’ or a red X for ‘no.’ If the answer is ‘no,’ it prevents unauthorized access to the system. This approach minimizes disruption for employees while adding an extra layer of security, especially considering that despite user training, individuals may still use passwords that have been compromised. Conducting a dark web scan for employees’ passwords is revealing, and MFA significantly strengthens the defense against potential breaches.
3. Vulnerability Assessments
Identifying your vulnerabilities is crucial for making informed business decisions regarding remediation. Without a clear understanding of your challenges, it’s challenging to assess and address risks effectively. It may sound a bit circular, but the key is gaining insight into your current position to formulate a forward-looking plan.
Conducting cybersecurity vulnerability assessments provides a straightforward method for examining your network. Utilizing automated tools, these assessments pinpoint common breaches and vulnerabilities. They identify issues like unpatched systems, absence of antivirus protection, or unnecessary local admin rights. These seemingly minor issues can be easily addressed through policies and remediations, effectively sealing significant security gaps in your network.
The assessment involves tasks such as patching, closing unused ports in your firewall, and implementing measures to reduce your attack surface, ultimately minimizing exposure. Since cybercriminals prefer easy targets, fortifying your network makes it less attractive to potential threats, prompting them to seek easier victims elsewhere.
Conclusion
In summary, cybersecurity is a foundational element for the overall health and sustainability of small businesses. It is not merely a technical requirement but an integral part of building trust, ensuring compliance, and protecting the core assets that drive the success of small enterprises in today’s digital landscape.





